Understanding Depression Symptoms: Chronic, CNS, Physiological Signs, and Treatment with Therapy
Depression is a widespread mental health disorder affecting millions worldwide, manifesting in various ways and impacting individuals physically, emotionally, and mentally. Recognizing depression symptoms early on is crucial for seeking help and treatment, improving overall quality of life. In this article, we will dive into various symptoms of depression, including chronic depression, CNS (central nervous system) depression, physiological symptoms, and more. We’ll also explore how therapy plays a key role in managing depression effectively.
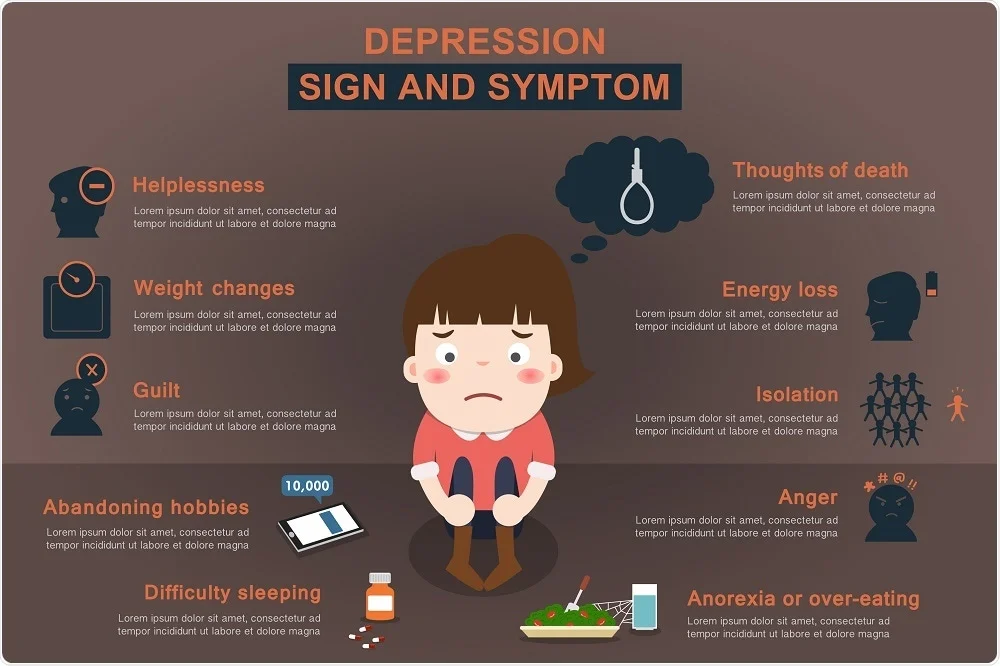

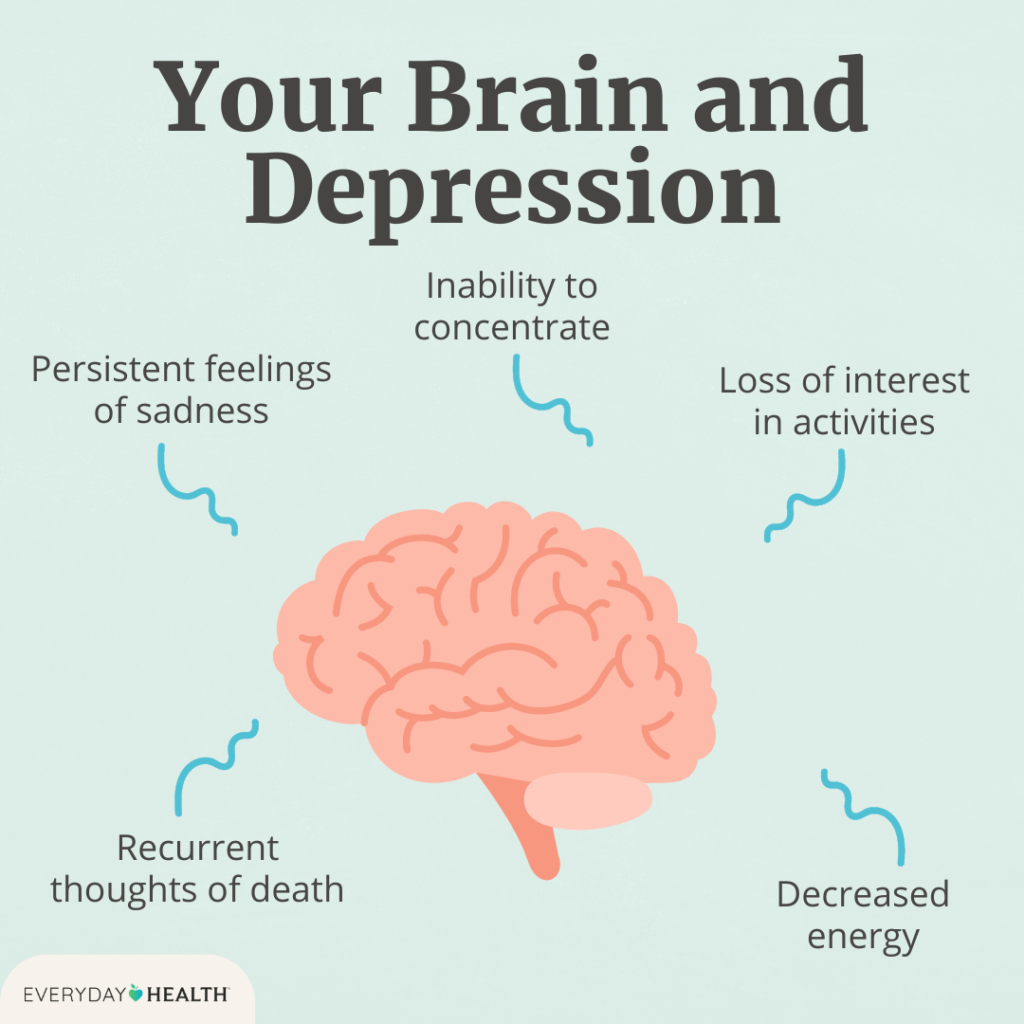
Chronic Depression Symptoms
Chronic depression, known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD) or dysthymia, is a long-term form of depression. Unlike major depressive disorder (MDD), chronic depression involves persistent, less intense symptoms that last for two years or more, deeply affecting daily life and relationships.
Common Chronic Depression Symptoms Include:
- Persistent Low Energy: Individuals with chronic depression often experience fatigue, even with adequate rest.
- Constant Sadness or Emptiness: Those with chronic depression may feel an ongoing sense of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness.
- Reduced Interest in Activities: A lack of interest in activities once enjoyed is a typical symptom, impacting hobbies and social interactions.
- Feelings of Guilt and Self-Criticism: Chronic depression can lead to feelings of guilt and self-doubt, affecting self-esteem.
- Sleep Issues: Difficulty sleeping, or sleeping too much, is a common symptom of chronic depression, further impacting energy levels.
Chronic depression may not appear as severe as other forms, but its long-lasting nature makes it essential to identify and address. Therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes medication are helpful approaches for managing chronic depression.
CNS Depression Symptoms
Central nervous system (CNS) depression refers to a reduction in brain activity, affecting physical and mental functions. Although commonly associated with substance use, CNS depression can occur in individuals with severe depression, leading to specific symptoms.
Common CNS Depression Symptoms Include:
- Slower Reaction Time: Depression can cause delayed physical and mental responses, making individuals feel sluggish.
- Reduced Alertness: Difficulty staying focused and alert can make it hard to engage fully with tasks.
- Drowsiness and Fatigue: Many people experience excessive tiredness due to CNS depression.
- Low Respiratory and Heart Rates: In more severe cases, CNS depression can reduce respiratory and heart rates, impacting overall energy and health.
CNS depression is a serious condition that may be intensified by alcohol or certain medications. If CNS depression symptoms appear, medical advice should be sought immediately to avoid risks and determine safe treatment methods.
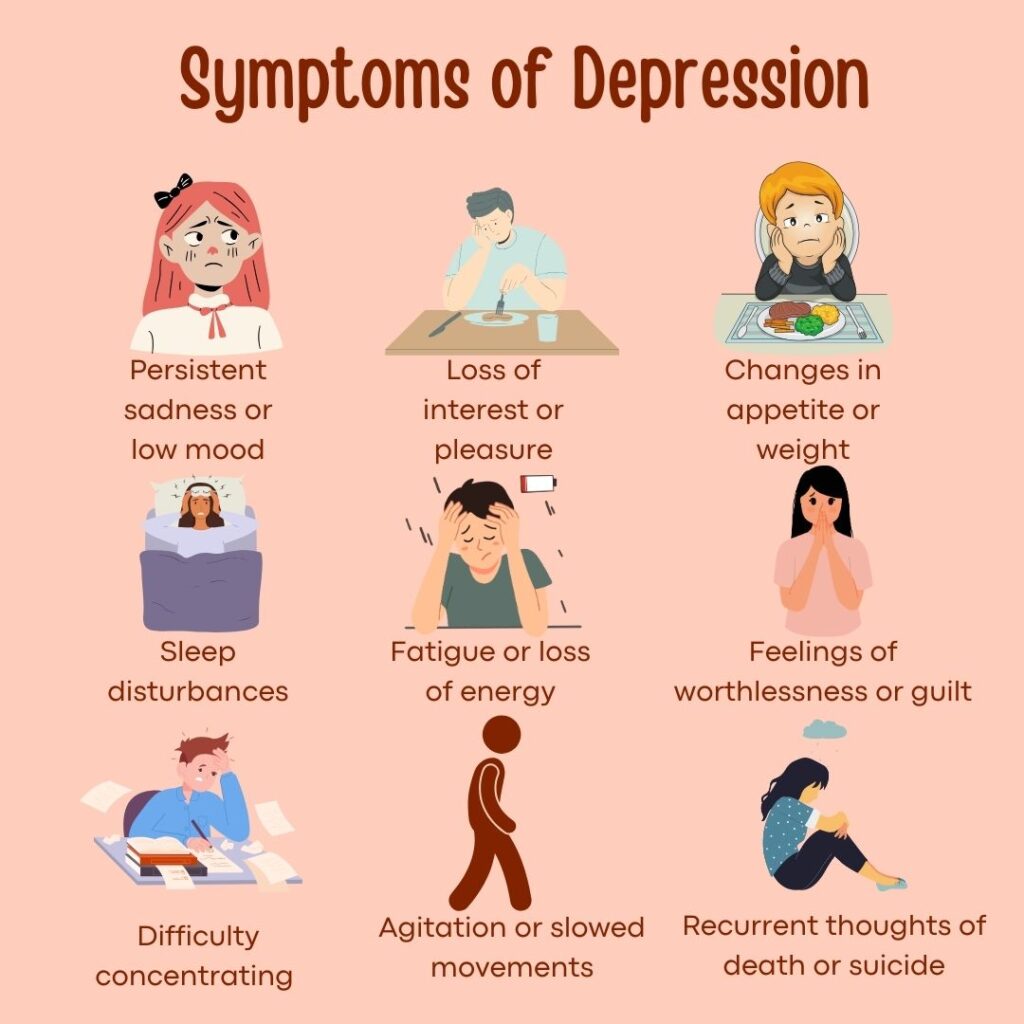
Depression Signs and Symptoms
Identifying the signs and symptoms of depression is essential, as they vary widely across individuals. Recognizing these indicators can lead to earlier diagnosis and intervention.
Key Signs and Symptoms of Depression Include:
- Persistent Sadness: An ongoing sense of sadness or hopelessness is one of the most recognizable symptoms of depression.
- Loss of Interest in Activities: People with depression may no longer find joy in activities they once loved.
- Increased Irritability: Frustration and irritability are common, especially in situations that would not usually cause stress.
- Chronic Fatigue and Sleep Issues: Depression frequently disrupts sleep, leading to insomnia or excessive sleep.
- Appetite Changes: Depression often results in changes in appetite, leading to weight gain or loss.
These signs and symptoms can disrupt everyday life and make even basic tasks feel overwhelming. Recognizing them and seeking help from a mental health professional can lead to effective treatment and recovery.
Depression Signs and Symptoms: Understanding the Difference
In medical terms, “signs” are observable behaviors or physical manifestations others can see, while “symptoms” are experiences reported by the individual. Here’s a breakdown of both:
Notable Signs of Depression Include:
- Visible Fatigue: Depression can make someone appear consistently tired or unmotivated.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding friends, family, or social situations may be noticeable to others.
- Decline in Productivity: Performance at work, school, or in personal projects may decrease significantly.
Common Symptoms of Depression Include:
- Feelings of Worthlessness: Persistent feelings of worthlessness or inadequacy.
- Physical Discomfort: Depression can lead to physical symptoms like body aches and digestive issues.
- Intense Guilt: Individuals may experience intense guilt over things that are beyond their control.
Understanding these signs and symptoms can help those affected receive timely support and help friends and family identify when a loved one needs help.

Physiological Symptoms of Depression
Depression often impacts physical health, causing symptoms that can be mistaken for unrelated medical issues. Recognizing these physiological effects can lead to a more comprehensive understanding and treatment.
Physiological Symptoms of Depression Include:
- Increased Pain Sensitivity: Depression can make individuals more sensitive to pain, especially chronic body aches.
- Frequent Headaches and Migraines: Depression is often linked to increased instances of headaches and migraines.
- Digestive Disturbances: Depression can impact digestive health, causing issues like nausea, constipation, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Muscle Tension: Many people with depression experience tension, especially in the neck and shoulders.
- Heart Health Concerns: Research links depression with higher risks of cardiovascular issues, possibly due to inflammation and stress.
Recognizing these physical symptoms can provide a fuller picture of depression’s impact and encourage seeking comprehensive care that addresses both mental and physical health.
How Does Therapy Help in the Treatment of Depression?
Therapy is one of the most effective treatments for managing depression. It allows individuals to explore their thoughts and feelings in a safe environment, learn coping strategies, and work through underlying issues contributing to depression.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a popular approach that identifies negative thought patterns and replaces them with positive, constructive thinking. This therapy equips individuals with tools to manage their emotions and reactions better.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): IPT focuses on improving relationships and social skills, which can be beneficial for people whose depression stems from interpersonal difficulties.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: This therapy examines unconscious thoughts and past experiences to resolve unresolved conflicts and underlying emotional pain.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy: Mindfulness techniques help individuals stay grounded in the present, reducing the anxiety and stress that often accompany depression.
- Group Therapy: Group therapy offers the chance to connect with others facing similar challenges, helping to reduce feelings of isolation.
Therapy can be a powerful tool in managing and overcoming depression. Working with a mental health professional allows individuals to receive tailored treatment and develop a personalized approach to recovery.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing and understanding the symptoms of depression, from chronic and CNS-specific symptoms to physiological effects, is essential for effective management. Identifying these signs early can make a significant difference, allowing individuals to seek help and take proactive steps toward improvement. Therapy offers various techniques that cater to unique needs, giving individuals the tools to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Depression is manageable, and with the right support and treatment, individuals can work toward a healthier, more balanced life. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider or mental health professional can be a crucial first step toward recovery.
1. What are the most common symptoms of depression?
The most common symptoms of depression include persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt, and sometimes thoughts of self-harm. These symptoms can vary in intensity, lasting for weeks or even months, and can significantly impact daily life.
2. How is chronic depression different from regular depression?
Chronic depression, also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD) or dysthymia, is a long-term form of depression with less intense but more enduring symptoms. Unlike major depressive disorder (MDD), where symptoms can be severe and may come in episodes, chronic depression persists for two or more years with a generally lower mood. Individuals with chronic depression might feel tired, lack self-esteem, and have low energy, which affects daily functioning over time.
3. Can physical symptoms be a sign of depression?
Yes, depression can manifest through physical symptoms such as headaches, digestive issues, chronic pain, and muscle tension. These physical symptoms often coexist with emotional symptoms and can make depression harder to diagnose, as people might initially seek treatment for physical ailments rather than psychological help.
4. What is CNS depression, and how does it relate to mental depression?
CNS (central nervous system) depression refers to a slowdown in brain activity that affects mental and physical functioning. While it is commonly caused by substances like alcohol or drugs, severe forms of mental depression can also slow down brain activity, leading to lethargy, slower reaction times, reduced alertness, and drowsiness. CNS depression requires immediate medical attention, particularly when linked with substance use.
5. How can therapy help in treating depression symptoms?
Therapy helps treat depression by providing coping strategies, exploring underlying causes, and altering negative thought patterns. Common approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) focus on changing harmful thoughts, while interpersonal therapy (IPT) and psychodynamic therapy address relational issues and past experiences that may contribute to depression. Therapy also offers a supportive environment, helping individuals understand and manage symptoms effectively






