Easy Ways to Calm Your Anxiety When Life Gets Tough
Discover effective treatments for anxiety and depression, including innovative therapies like ketamine, essential treatment goals, and the benefits of therapy. Explore an in-depth guide to better mental health management.
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health issues today, affecting millions of people worldwide. While they are distinct conditions, they frequently overlap, creating a cycle of stress and sadness that can feel overwhelming. This guide explores the complex relationship between anxiety and depression, examining treatment options, therapy, and medication, empowering you on your path to improved mental health.
Resistant Depression Treatment
For some people, traditional treatments like SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) or talk therapy may not alleviate symptoms. This condition, known as treatment-resistant depression (TRD), requires more specialized approaches. Below are some advanced treatments for those with TRD:
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): ECT uses brief electrical currents to stimulate the brain under anesthesia, which can help relieve severe symptoms of depression, especially when other treatments haven’t worked.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): TMS uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain regions of mood regulation. It’s non-invasive, typically well-tolerated, and can reduce symptoms for people who haven’t responded to medication.
- Ketamine Therapy: Ketamine is emerging as a fast-acting treatment for TRD. Administered via IV infusions or as a nasal spray, ketamine can quickly improve symptoms, making it a valuable option for those in acute distress.
Resistant depression treatments often work best in combination with lifestyle changes, nutrition support, and regular therapy. An individualized approach is essential, as mental health varies significantly from person to person.
Side Effects of Ketamine Treatment for Depression
While ketamine shows promise in treating TRD, it comes with potential side effects. It’s crucial to be aware of these before beginning treatment:
- Dissociation: One of the most common side effects, dissociation, involves feeling detached from oneself or the environment. This sensation typically fades a few hours after treatment.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These side effects are common but manageable, often mitigated by taking anti-nausea medication before treatment.
- Increased Blood Pressure: Ketamine may cause a temporary rise in blood pressure, so people with hypertension should discuss potential risks with their doctor.
- Headaches: Some people experience mild to moderate headaches after ketamine treatment. Staying hydrated and resting usually alleviates this discomfort.
Because ketamine is administered in a medical setting, healthcare professionals can monitor side effects, ensuring a safe treatment process. Regular assessments are crucial to maximize benefits and minimize risks.

Treatment for Depression: Traditional and Alternative Approaches
Depression treatment has evolved over the years, offering more options than ever. Here’s a look at some common and effective methods for treating depression:
- Medications: SSRIs, SNRIs (Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors), and atypical antidepressants are widely prescribed. These medications work by balancing brain chemicals related to mood regulation. However, they may take several weeks to show noticeable effects.
- Psychotherapy: Forms of psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), and Interpersonal Therapy (IPT), are essential tools for managing depression. These therapies help people change harmful thought patterns, improve emotional resilience, and better handle stress.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Exercise, nutritious food, and consistent sleep are powerful tools for improving mood. Mindfulness and meditation practices also help reduce anxiety, providing relief for people with both anxiety and depression.
- Alternative Therapies: Additional options include light therapy, acupuncture, and herbal supplements like St. John’s Wort. While more research is needed, these methods have shown benefits for some individuals.
A well-rounded approach, customized to the individual, often yields the best results in treating depression.
Treatment Goals for Depression
Establishing clear goals in depression treatment can provide a sense of direction and purpose. Here are some common goals in a depression treatment plan:
- Symptom Relief: The primary objective is reducing symptoms such as prolonged sadness, fatigue, and anxiety to improve daily functioning and quality of life.
- Restoring Daily Functioning: Depression can make it difficult to complete everyday tasks, affecting work, relationships, and personal well-being. A key goal is helping people regain control over these aspects of life.
- Building Coping Skills: Treatment often focuses on equipping individuals with tools to manage anxiety, stress, and depressive symptoms, empowering them to maintain stability even after active treatment.
- Preventing Relapse: Developing strategies for long-term mental health helps reduce the risk of relapse. Ongoing therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes maintenance medication play essential roles.
- Strengthening Social Connections: Depression can lead to isolation. Treatment plans often encourage rebuilding and maintaining relationships, which can provide emotional support and reduce loneliness.
Each person’s path to recovery is different, and treatment goals may evolve. A patient-centered approach ensures consistent and sustainable progress.
How Therapy Helps in the Treatment of Depression
Therapy plays a central role in managing depression, offering both immediate relief and long-term skills for better mental health. Here’s how therapy benefits people dealing with depression:
- Identifying Triggers: Therapy helps people understand the events, thoughts, or experiences that lead to depressive episodes. Awareness of triggers allows individuals to make proactive changes in their lives.
- Addressing Negative Thinking Patterns: Depression often brings about harmful thought patterns. Therapists guide individuals in reframing these thoughts, which can reduce feelings of hopelessness and foster more positive perspectives.
- Developing Coping Mechanisms: Therapy provides practical tools for dealing with stress, anxiety, and sadness. These coping skills are essential for managing mental health independently.
- Creating a Safe Space: Therapy offers a confidential, supportive environment where individuals can express their emotions without judgment, allowing them to process difficult feelings constructively.
- Building Social Support Networks: Therapists may recommend group therapy or support groups, helping individuals find a community of people who understand and support them. Social connection plays a key role in recovery.
Therapy’s purpose goes beyond addressing immediate symptoms; it’s about building a foundation for emotional resilience and well-being, ensuring individuals have the skills to manage mental health throughout their lives.
Final Thoughts
Anxiety and depression are challenging conditions, but understanding them and knowing about available treatment options can make a significant difference. From innovative therapies like ketamine to setting specific treatment goals, each approach offers hope for improved mental health. Treatment works best when it is personalized, using a mix of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes to meet individual needs.
Remember, healing is a journey, and progress can be gradual. With patience, self-compassion, and a well-structured treatment plan, those dealing with anxiety and depression can find relief and regain a sense of control in their lives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Anxiety
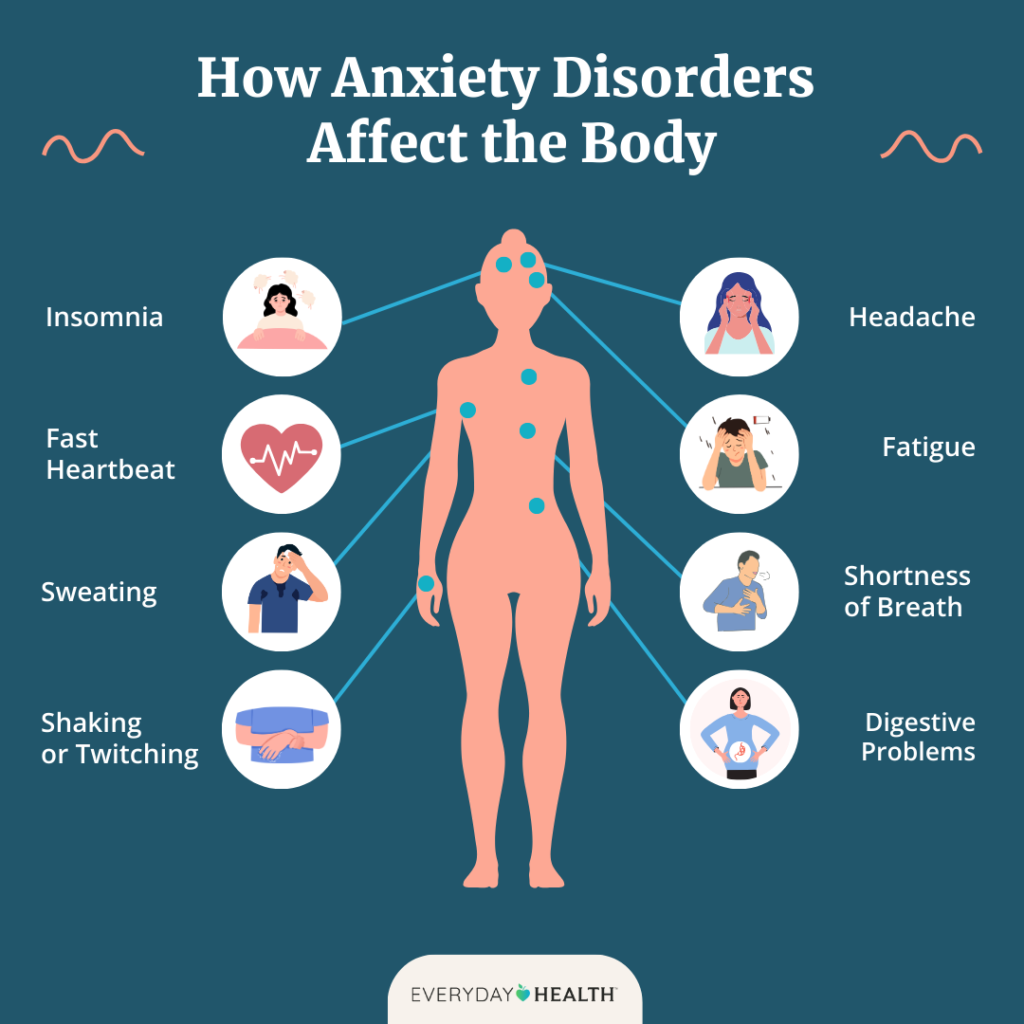
1. What are the common symptoms of anxiety?
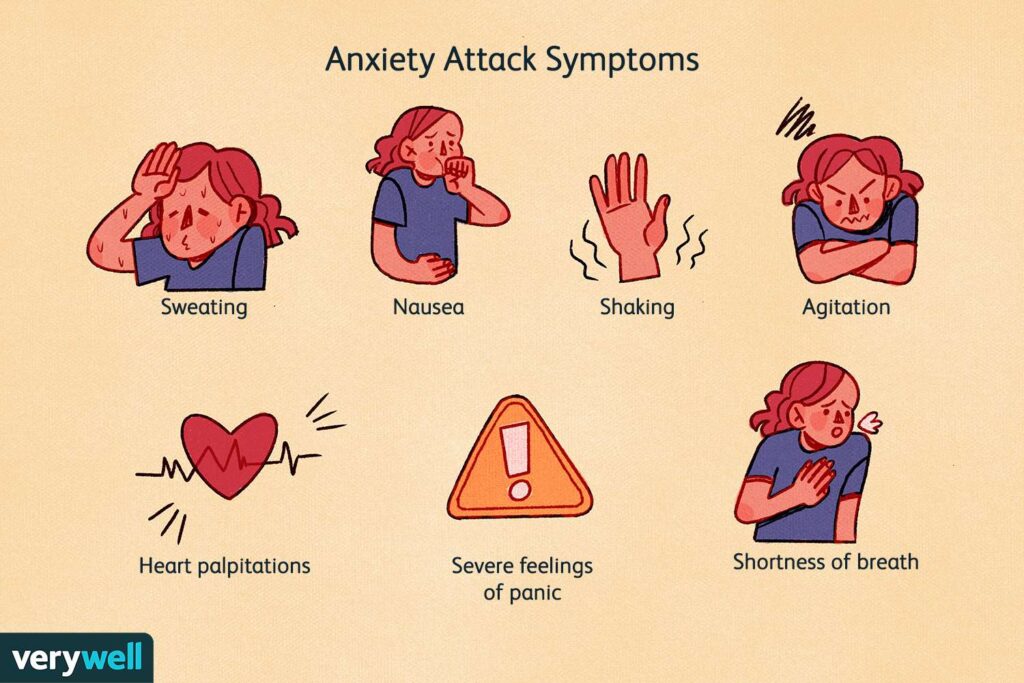
Anxiety symptoms can vary widely, but common ones include constant worry, restlessness, trouble concentrating, rapid heart rate, sweating, and physical tension. Some people may experience digestive issues, insomnia, or even panic attacks. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in managing anxiety effectively.
2. How is anxiety different from stress?
While stress is typically a response to an external trigger, such as a work deadline or a major life event, anxiety is often an internal reaction that persists even when there’s no immediate threat. Stress tends to subside once the situation resolves, but anxiety can linger, causing prolonged unease and interfering with daily activities.
3. Can lifestyle changes help reduce anxiety?
Yes, lifestyle changes like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and quality sleep can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, and limiting caffeine intake can also help. Building a supportive social network and finding time for hobbies or relaxation are key to maintaining mental well-being.
4. Are there natural remedies for managing anxiety?
Some people find relief from anxiety symptoms with natural remedies such as chamomile tea, valerian root, and magnesium supplements. Aromatherapy using essential oils like lavender can also have a calming effect. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before trying any supplements, as they can interact with medications.
5. When should I seek professional help for anxiety?
If anxiety is persistent, affects your daily functioning, or leads to panic attacks, it may be time to seek professional help. Therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and medication can be very effective in managing anxiety. A mental health professional can help you identify coping strategies and determine if further treatment is needed.







