10 Essential Facts About the Heart for a Healthier Life
Myocardial Infarction: Causes and Effects
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as heart attack, is a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the is blocked, usually due to a blood clot. This blockage prevents oxygen from reaching the muscle, leading to tissue damage or death. The most common cause of myocardial infarction is coronary artery disease, where plaque buildup narrows the arteries. Patients may experience intense chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea. Prompt medical attention is crucial, as delays in treatment can lead to irreversible heart damage or even death.
The aftermath of a myocardial infarction can be devastating, often leading to complications such as failure or arrhythmias. Early diagnosis and treatment, including medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical interventions, can help improve outcomes. Regular monitoring through tools like echocardiograms is vital for assessing the heart’s functionality post-attack. Raising awareness about the symptoms and risk factors is essential for preventing this life-altering condition.
Preventing myocardial infarction involves managing risk factors such as high cholesterol, hypertension, and smoking. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management play pivotal roles. By adopting these habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing a attack and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
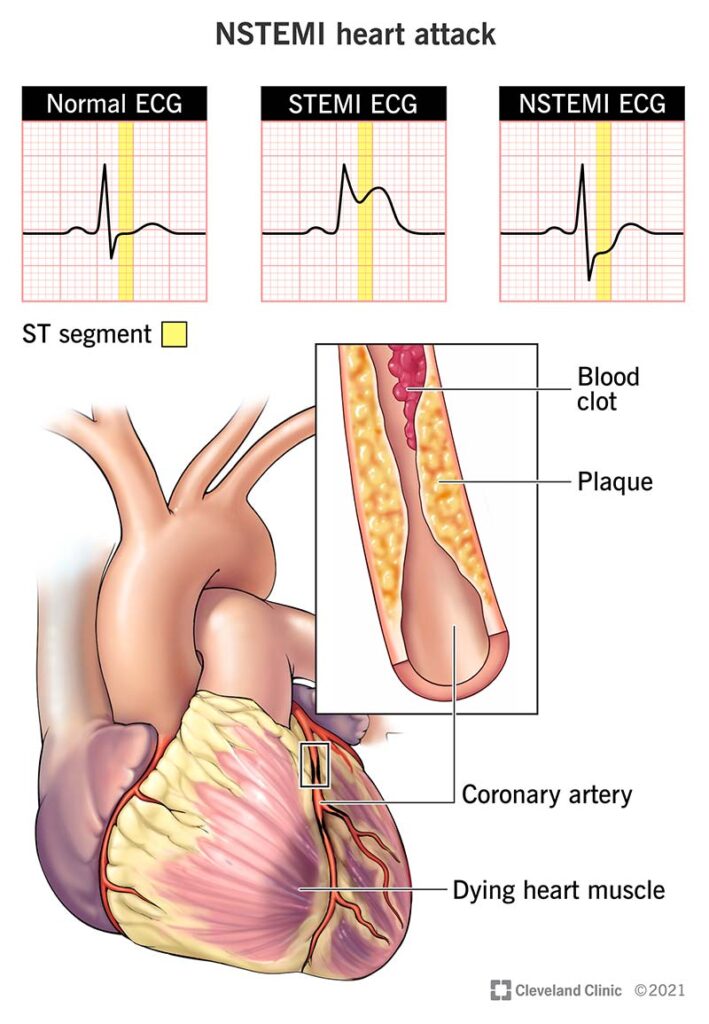
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms and Diagnosis
Congestive failure (CHF) is a chronic condition in which the cannot pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. This inefficiency leads to the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, liver, and other tissues, causing symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and ankles. CHF is often the result of underlying conditions like hypertension, myocardial infarction, or valve disorders, which weaken the pumping capacity over time.
The diagnosis of congestive failure requires a comprehensive evaluation, including physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies like echocardiograms. An echocardiogram is particularly valuable in assessing the structure and function, helping healthcare professionals identify the severity and underlying causes of CHF. Early diagnosis is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life.
Treatment for CHF often involves a combination of medications, such as diuretics and beta-blockers, alongside lifestyle changes like sodium restriction and increased physical activity. Advanced cases may require surgical interventions, such as valve repair or implantation of devices like pacemakers. By addressing the root causes and adhering to a tailored treatment plan, patients can manage CHF effectively.
Coronary Artery Disease: A Silent Threat
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the most prevalent causes of cardiovascular complications worldwide. It develops when the coronary arteries, responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This gradual narrowing reduces blood flow, often leading to symptoms such as chest pain, known as angina, or in severe cases, myocardial infarction.
Early detection of CAD is vital for preventing complications. Diagnostic tools like stress tests, coronary angiograms, and echocardiograms play a crucial role in identifying the presence and extent of the disease. Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, are essential first steps in managing CAD. Medications like statins and antiplatelet drugs are also commonly prescribed to reduce plaque buildup and prevent clot formation.
In severe cases of coronary artery disease, surgical interventions such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting may be required to restore blood flow. Raising public awareness about CAD and its risk factors is critical for reducing its prevalence and associated health burdens.
Echocardiogram: A Window to the Heart
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive imaging test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the structure and function. This diagnostic tool is indispensable in evaluating various conditions, including congestive heart failure, valvular diseases, and myocardial infarction. By providing real-time visuals, an echocardiogram helps physicians assess the pumping ability and detect abnormalities such as fluid accumulation or damaged heart muscles.
There are different types of echocardiograms, including transthoracic, transesophageal, and stress echocardiograms, each suited for specific diagnostic needs. The procedure is painless and typically takes 30 to 60 minutes. It is widely used in routine cardiac care and critical situations where quick and accurate assessment is needed.
The insights gained from echocardiograms guide treatment decisions, such as the need for medications, lifestyle changes, or surgical interventions. By enhancing our understanding of heart function, this test plays a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes.
Angina: Understanding Chest Pain
Angina is a symptom of reduced blood flow to the heart, often manifesting as chest pain or discomfort. It is a common indicator of underlying coronary artery disease. The pain may radiate to the arms, neck, or back and is typically triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress. While stable angina occurs predictably and resolves with rest, unstable angina is more severe and unpredictable, requiring immediate medical attention.
Managing angina involves addressing the root causes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Medications like nitroglycerin can provide quick relief by dilating blood vessels, and improving blood flow to the heart. Long-term management includes lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, surgical procedures like angioplasty.
Raising awareness about angina and its potential progression to serious conditions like myocardial infarction is essential. Recognizing the symptoms early can prompt timely intervention, preventing life-threatening complications.

Arrhythmia: When the Heart Beats Irregularly
Arrhythmias are irregularities in the heart’s rhythm, which can range from harmless to life-threatening. Common types include atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and ventricular tachycardia. Symptoms may include palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath, although some arrhythmias may remain asymptomatic. These conditions can result from electrolyte imbalances, myocardial infarction, or congenital heart defects.
Diagnosing arrhythmias often requires an electrocardiogram (ECG) or Holter monitoring to capture the heart’s electrical activity. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the arrhythmia, ranging from medications to electrical cardioversion or the implantation of pacemakers.
Preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions, can significantly reduce the risk of arrhythmias. Awareness and timely medical care are key to managing this condition effectively.
Cardiac Arrest: A Medical Emergency
Cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of heart function, often caused by an electrical malfunction that disrupts the heart’s rhythm. Unlike a heart attack, which is a circulation issue, cardiac arrest is an electrical problem that requires immediate intervention. Without prompt CPR and defibrillation, cardiac arrest can result in death within minutes.

Early signs of cardiac arrest include sudden collapse, unresponsiveness, and absence of a pulse. Emergency treatment focuses on restoring circulation and heart rhythm through advanced life support techniques. Long-term management may involve identifying and treating underlying causes, such as coronary artery disease or arrhythmias.
Public education on CPR and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) can save lives. By equipping communities with these skills, the survival rate of cardiac arrest victims can be significantly improved.
Congestive Cardiac Failure
Congestive cardiac failure, also known as heart failure, occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. This condition often results from diseases such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen ankles, and rapid weight gain. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life and prolong survival. Lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes surgical interventions are essential for managing this condition.
Congestive Cardiac Failure
Congestive cardiac failure, also known as heart failure, occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs. This condition often results from diseases such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen ankles, and rapid weight gain. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life and prolong survival. Lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes surgical interventions are essential for managing this condition.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart. This test helps assess the heart’s structure and function, detect abnormalities, and monitor conditions like heart failure, valve issues, or congenital heart defects. It is safe, painless, and often essential for forming a comprehensive treatment plan.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium, the thin sac surrounding the heart. This condition can result from infections, autoimmune diseases, or heart injuries. Symptoms often include sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or lying down, fever, and fatigue. Treatment usually involves managing the underlying cause and may include anti-inflammatory medications or antibiotics.
Normal Heart Rate
A normal resting heart rate typically ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute (BPM). Factors such as age, fitness level, and activity can influence this range. Monitoring your heart rate can provide insights into your cardiovascular health. For example, a consistently high or low heart rate might signal an underlying condition that warrants medical attention.
High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease. It occurs when there is an excess of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol, in the blood. This can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and, if needed, taking prescribed medications can help manage cholesterol levels effectively.
Angiogram
An angiogram is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the blood vessels. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream and taking X-ray images. This test is crucial for identifying blockages or narrowing in the arteries that may lead to chest pain, heart attacks, or other complications. Angiograms often guide decisions regarding treatments like angioplasty or bypass surgery.

Heart Failure Symptoms in Women
Heart failure symptoms in women can sometimes differ from those in men, making awareness critical for early detection. Women may experience atypical symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath during routine activities
- Swelling in the ankles or abdomen
- Nausea or lack of appetite
These symptoms are often subtle and easily overlooked, highlighting the importance of regular checkups and prompt attention to any unusual changes in health.
What are the common signs of an unhealthy heart?
Common signs of an unhealthy heart include chest pain, shortness of breath, and irregular “Create a high-resolution image symbolizing heart health and care. The image should feature a red heart symbol surrounded by a glowing protective shield, with hands gently cradling the heart to symbolize care and nurturing. Include a soft, gradient background in shades of blue and white, evoking calm and trust. Add subtle medical elements, such as a heartbeat line or stethoscope, integrated tastefully into the design. The overall feel should be modern, and clean, and promote wellness and healthcare. beat, fatigue, swelling in the legs or feet, and dizziness. If you experience these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately, as they could indicate serious issues.
How can I improve my heart health naturally?
You can improve your health naturally by eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Regular exercise, managing stress, avoiding smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting enough sleep are also crucial.
What are the best foods for heart health?
The best health foods include leafy greens, fatty fish like salmon, nuts, seeds, whole grains, berries, avocados, and legumes. These foods are rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber, which support function.
What are the early warning signs of a heart attack?
Early warning signs of an attack include chest discomfort or pressure, pain that spreads to the arms, neck, jaw, or back, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, and cold sweats. Prompt medical attention can save lives.
What is the connection between stress and heart health?
Chronic stress increases the risk of disease by raising blood pressure, causing inflammation, and encouraging unhealthy habits like overeating or smoking. Managing stress through meditation, exercise, or hobbies can protect your







